UPSC full form: There are many competitive exams that are conducted by UPSC. The full form of UPSC is Union Public Service Commission. Most of the career aspirants preparing for Central Government jobs conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) called Civil Service Exams (CSE) IAS, CDS, NDA, IFS, etc. The UPSC full form is the Union Public Service Commission which conducts Sarkari exams for the Union Government jobs. In this article, we have discussed the details of all Union Government jobs and Central government exams that UPSC conducts and the eligibility criteria, recruitment process, exam pattern, salary, etc. below.
UPSC is a national-level recruitment body for various competitive exams responsible for recruitment to 24 services in general under the Central and State Governments of India. The UPSC Exam is one of the toughest exams in India.
Table of Contents

What is UPSC full form?
Most of the candidates preparing for sarkari jobs know the full form of UPSC in Hindi and English. The UPSC full form in Hindi is संघ लोक सेवा आयोग. And the UPSC full form in English is the Union Public Service Commission. The Central government jobs aspirants who are looking for elite sarkari naukri try their destiny with UPSC exams.

The UPSC is a government sarkari jobs recruiting agency for different services and posts under Central Government. One of those services is UPSC Civil Services. The Union Public Service Commission conducts CSE exam every year by releasing IAS exam notification. You knew the UPSC full form here, let’s know the history of UPSC next.
Full Form of UPSC: History of Union Public Service Commission
The UPSC full form is mentioned above. Let’s know about the history of UPSC which conducts various sarkari exams for government jobs. For the first time a Civil Service Commission was set up in 1854 in London on recommendation of Lord Macaulay’s report of the British Parliament’s Select Committee. It was set up to replace East India Company’s patronage system by a permanent Civil Service based on merit system of recruitment. As a result the merit based competitive exams were started in 1855.
The origin of the Public Service Commission (PSC) in India goes to the First Dispatch of Government of India on March 5, 1919 on Indian Constitutional Reforms. However, the Public Service Commission was finally established on October 1, 1926 in India on the basis of the Government of India Act, 1919, Section 96 (C) and Lee Commission’s recommendation for the same in 1924. It consisted of its first Chairman – Sir Ross Barker and 3 other members.
The Public Service Commission became the Federal Public Service Commission on April 1, 1937 with the provision of the Government of India Act, 1935. The Act of 1935 also established a Provincial Public Service Commission for each province (state) or group of provinces.
Finally the Federal Public Service Commission was renamed as the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) when the Constitution of India was inaugurated on January 26, 1950. As a result the Chairman and Members of the Federal Public Service Commission became Chairman and Members of the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) by virtue of Clause (1) of Article 378 of Indian Constitution. Thus, along with the UPSC full form you knew about the history of Union Public Service Commission. Let’s come to know some other UPSC related abbreviations full form next.



UPSC Full Form: Sarkari Jobs IAS, IPS, NDA, CDS Stand for
The Union Public Service Commission is UPSC full form. The UPSC conducts various competitive exams for sarkari jobs like CSE, IAS, IPS, IFS, IFoS, IRS, NDA, CDS, CAPF, CISF, etc. The UPSC aspirants who are preparing for government jobs fill the UPSC application form for sarkari exams when their notification is released. The CSE, IAS, and other jobs and services of UPSC full form are given in the table below.
Full Form of UPSC, CSE, IAS, etc.
UPSC Jobs/Exams Short Form | UPSC Exam/Job/Service Full Form |
UPSC full form | Union Public Service Commission |
CSE full form | Civil Services Exam |
IAS full form | Indian Administrative Service |
IPS full form | Indian Police Service |
IFS full form | Indian Foreign Service |
IFoS full form | Indian Forest Service |
NDA & NA full form | National Defence Academy & Naval Academy |
CDS full form | Combined Defence Service |
CAPF full form | Central Armed Police Forces |
CISF full form | Central Industrial Security Force |
SCRA full form | Special Class Railway Apprentice |
IES/ES full form | Indian Engineering Service |
CMS full form | Combined Medical Service |
IES full form | Indian Economic Service |
ISS full form | Indian Statistical Service |
EPFO full form | Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation |
Constitutional Provisions of UPSC (Union Public Service Commission)
As mentioned above about the UPSC full form here you will know Constitutional provisions of UPSC. All about the UPSC is placed in Part 14 of Indian Constitution which deals with Union and state services (Articles 315 to 323). It is kept under Article 315 for conducting sarkari exams to fill up vacancies in the Union Government. The detailed constitutional provisions of UPSC in the Constitution of India are as follows:
- Art. 315: A Public Service Commission for the Union and the states.
- Art. 316: Provision of appointment and terms of office.
- Art. 317: Provisions of removal and suspension of Public Service Commission’s members.
- Art. 318: Provisions related to regulation of service conditions of members and staff.
- Art. 319: Provisions related to prohibition of offices by members after ceasing as member.
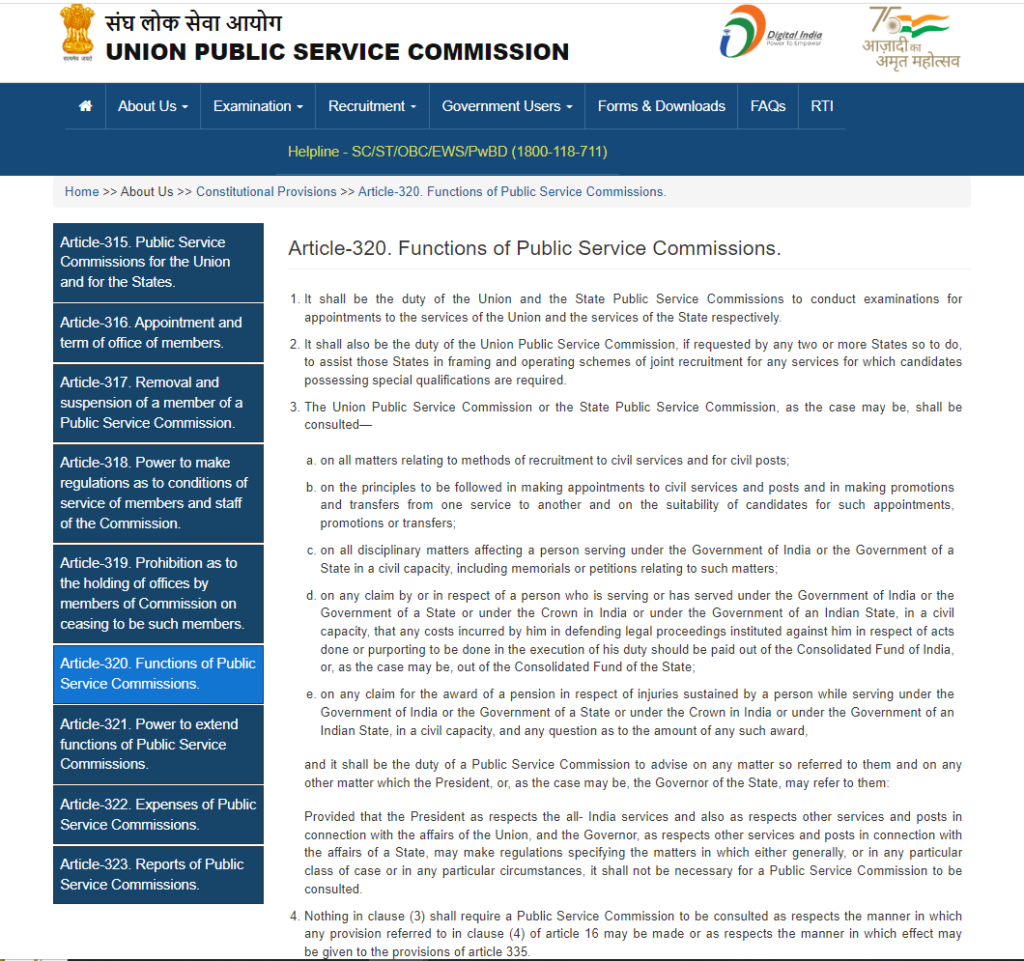
- Art. 320: Provisions of Public Service Commissions’ functions.
- Art. 321: Provisions of extension of Public Service Commissions’ functions.
- Art. 322: Provisions related to finance and expenses of Public Service Commissions.
- Art. 323: Public Service Commissions’ Reports
We have discussed UPSC full form, its history, and constitutional provisions, next will discuss UPSC functions.
Functions of UPSC: Art. 320
The UPSC’s functions are to notify and conduct Sarkari exams every year for government jobs and services of the Union government. The UPSC assists states in framing and operating joint recruitment schemes for any Sarkari jobs and services if requested by any two or more states to do so. The functions of UPSC are providing advice on matters related to:
- Methods of recruitment to Indian civil services and for civil posts.
- Principles of appointment, promotion, and transfers of services and posts.
- Disciplinary matters related to persons serving under the Government of India.
- Claim by a person serving or has served under the Government of India.
- Any claim for award of a pension in respect of injuries sustained during service.
UPSC Recruitment Process by Conducting Sarkari Exams
The career aspirants preparing for government jobs should have the knowledge of Sarkari exams conducted by the UPSC. There are more than thirteen government exams which the UPSC conducts for the recruitment and appointment in services under the Union Government. UPSC conducts a single exam in the name of Civil Service Exam (CSE) for more than 25 services and posts as per vacancies in different Ministries and departments of Union Government. The Sarkari jobs aspirants can fill up the UPSC application form for different government exams by visiting the official website – upsc.gov.in.
Additionally, there are other posts and services for the UPSC releases notification and conducts exams every year. Here is a list of different government exams for different Sarkari jobs conducted by the UPSC:
- UPSC Civil Services Exam (CSE) for IAS, IFS, IPS, IRS, etc. officers posts
- Indian Forest Service (IFoS) Exam
- Engineering Service (ES) Exam
- Indian Medical Service (IMS) Exam
- Indian Economic Service (IES) Exam
- Indian Statistical Service (ISS) Exam
- Combined Geo-Scientist and Geologist Exam
- Combined Defence Services (CDS) Exam
- National Defence Academy & Naval Academy (NDA & NA) Exam
- Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) Exam
- Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) Exam
- Special Class Railway Apprentice (SCRA) Exam
- Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) Exam
UPSC Eligibility Criteria for CSE
There are various parameters of eligibility criteria for the Central government services conducted through UPSC exams which aspirants must meet to apply to appear in different sarkari exams for government jobs including Civil Services. These UPSC eligibility criteria IAS, IPS, etc. are given in the table below:
UPSC IAS Exams | Eligibility Criteria |
Nationality | Indian citizen for IAS, IPS, IFS For other Services Indian citizen, subject of Nepal or Bhutan, Tibetan refugee… |
Age limits on 1st August of appearing year | General: 21– 32 years OBC: 21 – 35 Years SC/ST: 21 – 37 Years PwBD: 21 – 42 Years |
Educational Qualification | Graduation degree from Central/State University |
Number of Attempts | General category: 6 OBC category: 9 SC/ST category: Unlimited PwBD: 9 for GL/EWS/OBC |
UPSC CSE Exam Pattern
The candidates preparing for Sarkari jobs must be aware of UPSC IAS exam pattern. The UPSC civil services recruitment process is based on prelims and mains exam pattern. The IAS prelims exam consists of 2 papers of 200 marks each. The CSE prelims is a screening test to qualify for the mains exam. The mains exam consists of a written exam and personality test i.e. interview for final selection.
The UPSC Civil Services mains written exam consists of 9 papers of 2650 marks. The Personality Test i.e. interview is conducted for 275 marks by UPSC interview board.
Direct link for IAS Exam Dates 2022: Click here
UPSC Salary
The government jobs seekers preparing for Sarkari exams mainly conducted by the UPSC are first attracted by the salary of various posts and services. However, the UPSC salary varies as per post, service and the level for which selected candidates join. The salary of Central Government’s employees recruited through UPSC exams is based on the Seventh Pay Commission recommendations. In addition to salary they also get different allowances such as house rent allowance (HRA), dearness allowance (DA), travel allowance (TA), medical allowance, special allowance, and many other perks and facilities
Share this article with your friends, family and fellow colleagues to oblige them!
Also read IAS full form, history, work portfolio, etc.: Click
Important Articles
| NEET Toppers 2022 List |
UPSC Full Form: FAQs
Q. What is UPSC full form?
Ans. UPSC full form is Union Public Service Commission.
Q. Is IAS and UPSC same?
Ans. UPSC full form is the Union Public Service Commission. It is a Central Government recruitment agency which conducts exams for Civil Services like IAS, IPS, IFS, ect. Whereas the IAS full form is Indian Administrative Service. So UPSC and IAS are not the same.
Q. Who is eligible for the UPSC exam?
Ans. Candidates preparing for sarkari jobs who have a graduate degree and 21 years minimum age but not more than 32 years are eligible for the UPSC Civil Services Exam.
Q. What is full form of UPSC?
Ans. The acronym UPSC stands for Union Public Service Commission. It is responsible for conducting examinations to select qualified candidates for various positions within the Indian Government.
Q. Who is UPSC topper 2022-23?
Ans. UPSC topper 2022-23 is Ishita Kishore. She has secured the first rank in the Civil Services examination 2022. Ishita Kishore is followed by Garima Lohia, Uma Harathi N, and Smriti Mishra.
Q. What is UPSC job
Ans. UPSC is a Union Government agency which conducts exams for sarkari jobs such as Civil Services IAS, IPS, IFS etc. and also for Defence like NDA, CDS, and others.
Q. What is IAS salary?
Ans. The salary of an IAS officer is based on the 7th Pay Commission’s recommendation. It starts with a basic salary of Rs 56100 with other allowances for SDM post.
Q. How many attempts are there in UPSC?
Ans. The maximum attempts for general category candidates are 6 up to 32 years of age in UPSC IAS exam.
Q. Can final year students apply for UPSC?
Ans. Yes, final year students can apply for the UPSC CSE exam. But he or she should pass the final year exam to be eligible with a graduation level degree at documents verification.
Q. What is the maximum age limit for UPSC?
Ans. The upper age limit for General category candidates is 32 years. But it is 35 years for OBC and 37 years for SC/ST candidates.
Q. Who is youngest IAS in India?
Ans. Ansar Shaikh is the youngest IAS officer of India who cracked Civil Services exam at the age of 21 years.
Q. What is IAS full form in English?
Ans. IAS full form in English is Indian Administrative Service.
Q. What is IAS full form in Hindi?
Ans. IAS full form in Hindi is भारतीय प्रशासनिक सेवा.
Q. What is IPS full form?
Ans. IPS full form is Indian Police Service.

